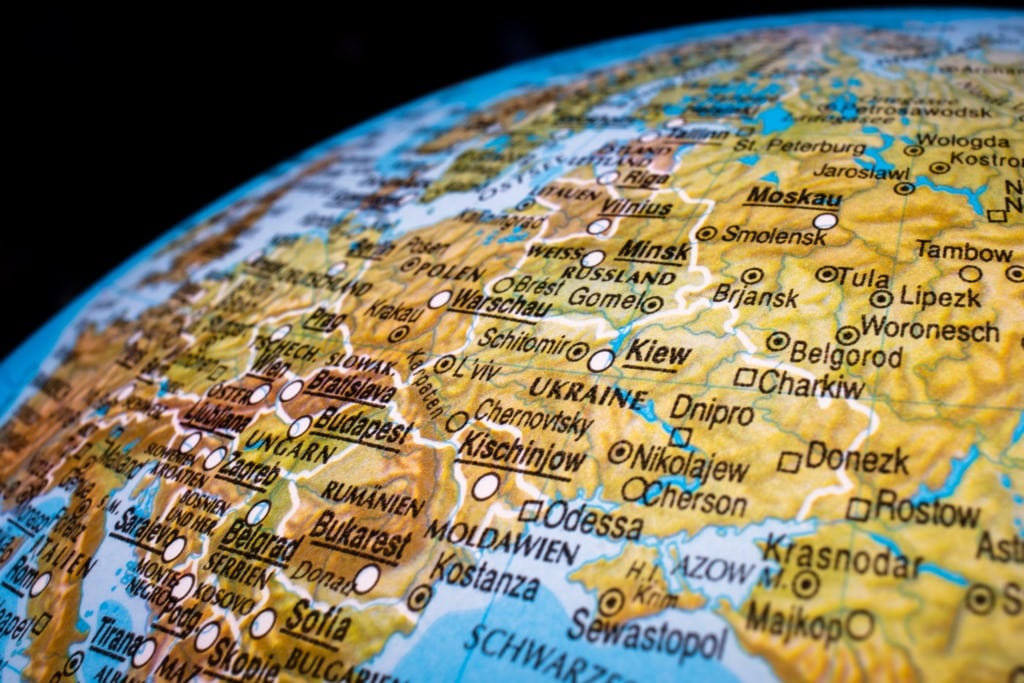
Serving Defendants in Ukrainian Territory Occupied by Russia
Both Russia and Ukraine are member states of the 1965 Convention on the Service Abroad of Judicial and Extrajudicial Documents in Civil or Commercial Matters (Hague Service Convention (HSC)). After Russia occupied the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and its capital city, Sevastopol, and exercised control over certain areas of Ukraine (the “Occupied Areas”), Ukraine filed…
Continue ReadingOral Argument on Personal Jurisdiction Today
The Supreme Court will hear oral argument today in Mallory v. Norfolk Southern Railway, a personal jurisdiction case in which the defendant “consented” to general jurisdiction in Pennsylvania based on a corporate registration statute. Although Mallory itself involves no transnational facts, the case could have important implications for foreign defendants. Pennsylvania’s registration and long-arm statutes,…
Continue ReadingSanctions and Terrorism
We have launched a new topic page on sanctions and terrorism. Sanctions are a critically important and highly controversial tool of foreign policy for many countries, especially the United States. Many sanctions do not result in litigation. Some do, however, and sanctions cases can produce very large judgments, especially in terrorism-related cases. Sanctions litigation also…
Continue ReadingSupreme Court to Decide Extraterritorial Reach of Trademark Statute
Today the Supreme Court granted review in Abitron Austria GmbH v. Hetronic International, Inc. to consider when the federal trademark statute, known as the Lanham Act, applies extraterritorially. In Steele v. Bulova Watch (1952), the Court held that the act applied extraterritorially to the infringement of a U.S. trademark in Mexico. But lower courts have developed different tests for implementing Steele, creating a…
Continue ReadingMore on the Validity of the PDVSA 2020 Bonds
Governments with no realistic prospect of paying their debts often gamble for redemption, trying desperately to avoid default. Political leaders, with good reason, fear that a debt default will get them thrown out of office. But in trying to hold power, sometimes by borrowing even more, they often make matters worse for the country and…
Continue ReadingNew Scholarship on the FSIA
Vivian Grosswald Curran (University of Pittsburgh) has a draft article up on SSRN entitled Nazi Stolen Art: Uses and Misuses of the Foreign Sovereign Immunities Act. Many important FSIA cases have involved great works of art stolen by the Nazis including the Supreme Court’s 2003 decision in Altmann v. Republic of Austria concerning the ownership…
Continue ReadingSecond Circuit Again Limits Extraterritorial Reach of Commodity Exchange Act
In Laydon v. Coöperatieve Rabobank U.A., the Second Circuit once again held that the Commodity Exchange Act (CEA) does not apply to futures contracts traded on U.S. exchanges that are tied to the values of foreign commodities. Although the transactions in this case undoubtedly occurred in the United States, the court held that the claims…
Continue ReadingA Primer on International Comity
The Supreme Court in Hilton v. Guyot (1895) famously defined international comity as “the recognition which one nation allows within its territory to the legislative, executive or judicial acts of another nation.” That definition is incomplete, however, as comity encompasses much more than the recognition of foreign acts. The Restatement (Fourth) of Foreign Relations Law…
Continue ReadingSDNY Rejects Immunity for Former Diplomat in Trafficking Case
To ensure that diplomats can perform their functions without harassment, international law grants them broad immunity from the criminal and civil jurisdiction of the state to which they are accredited. Unfortunately, some diplomats seem to treat such immunity as a license to abuse their domestic servants. Earlier this year, Ingrid (Wuerth) Brunk reported on a…
Continue ReadingCert Petition Highlights Split on Extraterritorial Application of Civil RICO
In RJR Nabisco v. European Community (2016), the Supreme Court held that RICO’s civil cause of action requires a domestic injury to business or property. The Court noted, however, that “[t]he application of this rule in any given case will not always be self-evident, as disputes may arise as to whether a particular alleged injury…
Continue Reading