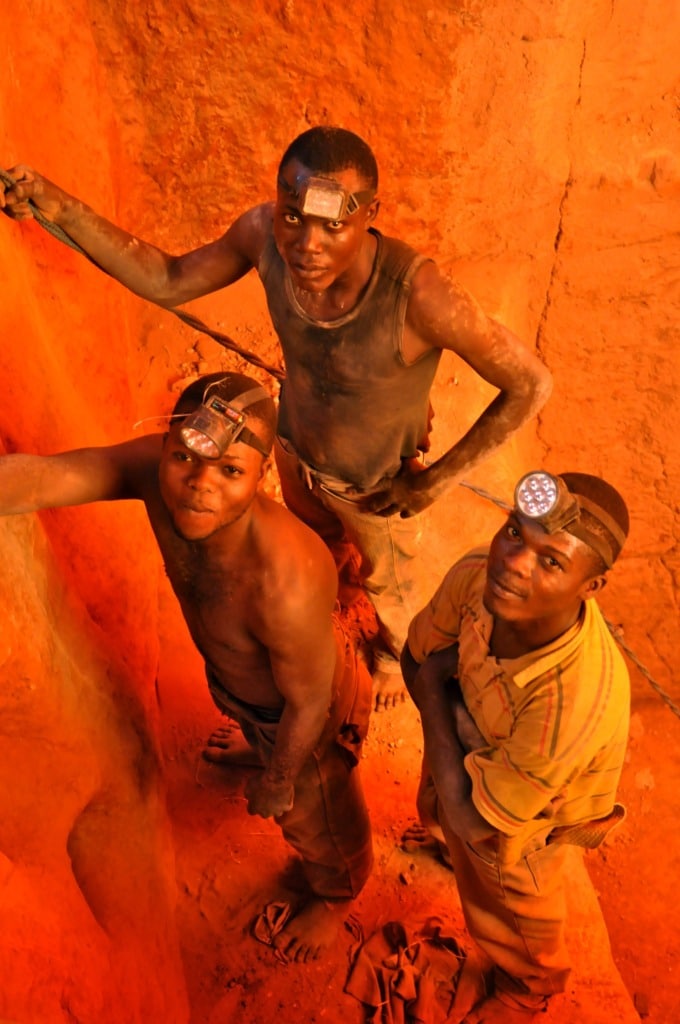
Does the TVPRA Apply Extraterritorially? Thoughts on the U.S. Chamber of Commerce Amicus Brief in Doe v. Apple
As the U.S. Supreme Court has repeatedly limited the scope of the implied cause of action under the Alien Tort Statute (ATS), victims of human rights abuses have looked to other U.S. statutes for remedies. One of these is the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA), which creates a civil remedy against perpetrators and others…
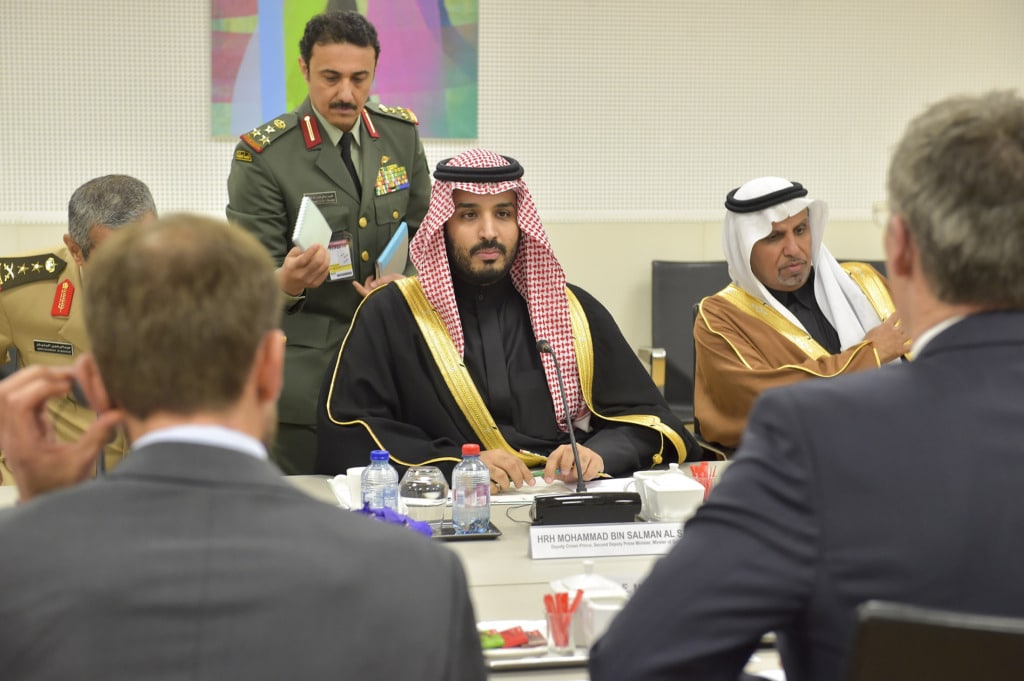
Continue ReadingDistrict Court Dismisses Another Case Against MBS for Lack of Personal Jurisdiction
Two weeks ago, while King Salman was appointing Crown Prince Muhammad bin Salman (MBS) as Prime Minister of Saudi Arabia in an apparent bid to secure him head-of-state immunity in a suit brought by Jamal Khashoggi’s widow, the judge in a different case quietly dismissed another plaintiff’s claims against MBS for lack of personal jurisdiction….
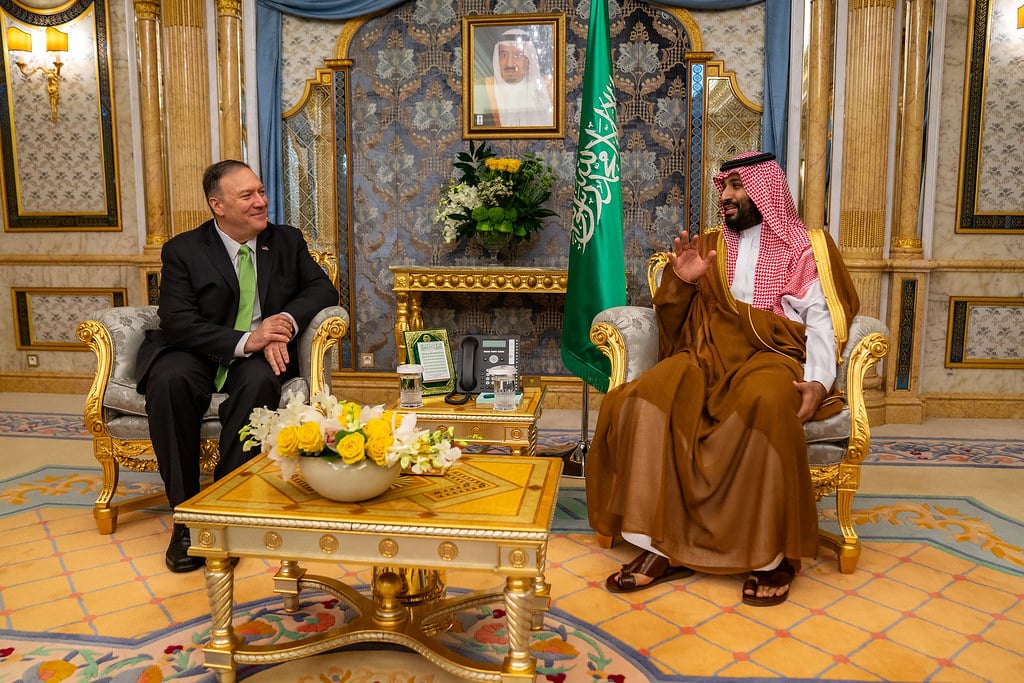
Continue ReadingMBS’s Appointment as Saudi Prime Minister Gives Him Head-of-State Immunity
On Tuesday, King Salman appointed Crown Prince Muhammad bin Salman (MBS) as Prime Minister of Saudi Arabia. The appointment makes MBS Saudi Arabia’s head of government, thereby entitling him to “head of state” immunity under U.S. law and customary international law. The appointment comes just days before an October 3 court deadline for the U.S….
Continue ReadingIs MBS Entitled to Head of State Immunity?
Editor’s Note: This article also appears in Just Security. In 2018, Saudi security agents brutally murdered journalist Jamal Khashoggi at Saudi Arabia’s consulate in Istanbul, Turkey. U.S. intelligence agencies concluded that Crown Prince Muhammad bin Salman (MBS) approved the operation. In 2020, Khashoggi’s widow and a non-profit organization that he helped found sued MBS and…
Continue ReadingThrowback Thursday: The Human Rights of Foreign Sailors
Litigation in U.S. courts involving gross misconduct committed outside the United States by non-U.S. actors did not begin with the revival of the Alien Tort Statute in the 1980s. In the earlier era of global trade that centered around maritime commerce, U.S. admiralty courts at times remedied—often with moral outrage—wrongs committed on the high seas….
Continue ReadingHas the Alien Tort Statute Made a Difference?
In a globalized and interconnected world, human rights litigation has, by necessity, become transnational. For decades, the Alien Tort Statute (ATS) was viewed as a beacon of American justice for foreign victims of human rights violations. However, a series of Supreme Court decisions—most recently the paired cases of Nestlé USA, Inc. v. Doe and Cargill,…
Continue ReadingSection 230 and the Presumption Against Extraterritoriality
The Ninth Circuit opinion in Gonzalez v. Google (2021) raises important questions about how the presumption against extraterritoriality applies to immunity defenses invoked by social media companies under 47 U.S.C. § 230.Section 230 shields internet companies from civil liability for user-generated content hosted on their platforms. Gonzalezholds, effectively, that there is no conceivable application of…
Continue ReadingA Primer on Human Rights Litigation
Modern human rights law developed in response to the events of the World War II, although it has earlier precursors. In 1948, the U.N. General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, a non-binding declaration. More than seventy human rights treaties followed, including the Genocide Convention, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights,…
Continue ReadingThe ATS Clarification Act Can Protect Human Rights and Level the Playing Field for U.S. Businesses
As previously reported on TLB, Senators Durbin (D-IL) and Brown (D-OH) recently introduced the Alien Tort Statute Clarification Act (ATSCA), which, if passed, will clarify the extraterritorial reach of the Alien Tort Statute (ATS) and expand the statute’s jurisdiction to cover all defendants “present in” the United States. The ATS is one of our nation’s…
Continue ReadingKashef v. BNP Paribas SA Overcomes the Forum Non Conveniens Hurdle
In Kashef v. BNP Paribas SA, Judge Alvin K. Hellerstein in the Southern District of New York recently denied the defendants’ motion to dismiss for forum non conveniens. The order allows plaintiffs to continue to pursue their claims against BNP Paribas S.A. and its U.S.-based subsidiary and New York branch (“BNPP”) for their role in…
Continue Reading