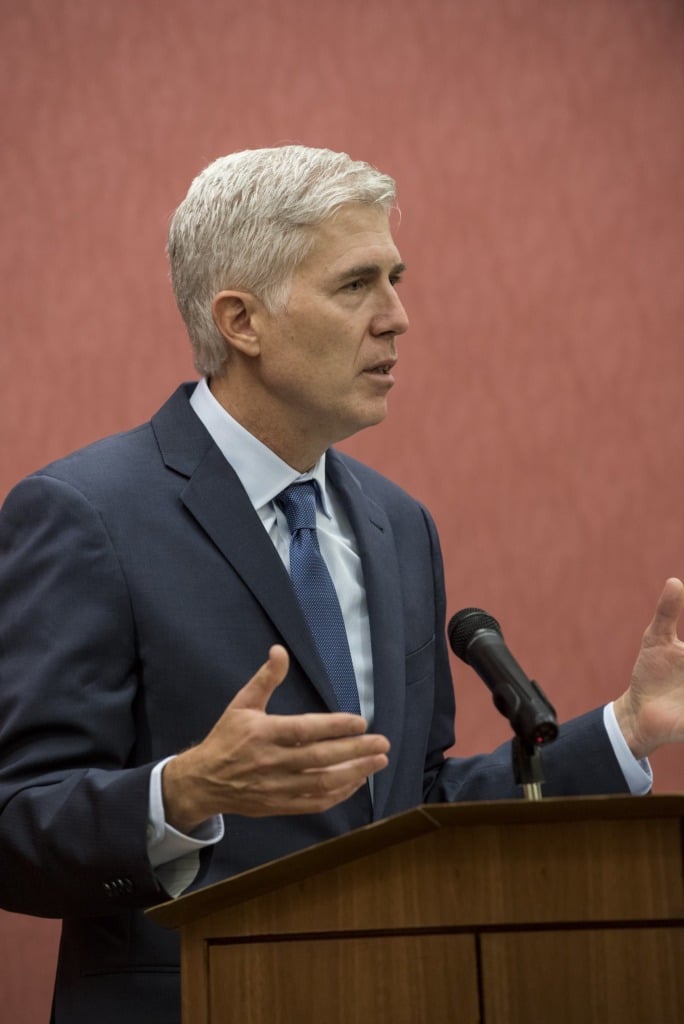
Dear Justice Gorsuch: There’s No Reason to Worry About the Remand in Halkbank
In Turkiye Halk Bankasi A.S. v. United States (Halkbank), the Supreme Court held that the Foreign Sovereign Immunities Act (FSIA) does not apply to criminal proceedings. The Court remanded the case to the Second Circuit to reconsider Halkbank’s claim of common law immunity. Justice Gorsuch, joined by Justice Alito, wrote a partial dissent. He would…
Continue ReadingSupreme Court Oral Argument in Extraterritorial RICO Case Marked by Confusion
The Supreme Court heard oral argument last week in Yegiazaryan v. Smagin and CMB Monaco v. Smagin, two cases testing when civil RICO can be used to help enforce a foreign arbitration award. Because I have described the facts in a previous post, I will be brief here. Smagin and Yegiazaryan are Russian citizens who…
Continue ReadingChina’s Draft Law on Foreign State Immunity—Part II
In December 2022, Chinese lawmakers published a draft law on foreign state immunity, an English translation of which is now available. In a prior post, I looked at the draft law’s provisions on immunity from suit. I explained that the law would adopt the restrictive theory of foreign state immunity, bringing China’s position into alignment…
Continue ReadingThrowback Thursday: Kiobel v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co.
Ten years ago this week, the U.S. Supreme Court handed down its decision in Kiobel v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., applying the presumption against extraterritoriality to the implied cause of action for human rights violations under the Alien Tort Statute (ATS). In Kiobel, the Court began to whittle down the cause of action it had…
Continue ReadingPreview of Supreme Court Argument in Civil RICO Extraterritoriality Case
On April 25, the U.S. Supreme Court will hear oral argument in Yegiazaryan v. Smagin and CMB Monaco v. Smagin, which ask how RICO’s private right of action applies to intangible property, in this case a California judgment confirming a foreign arbitral award. The cases have important implications not just for civil RICO but also for international arbitration….
Continue ReadingChina’s Draft Law on Foreign State Immunity Would Adopt Restrictive Theory
On the question of foreign state immunity, the world was long divided between countries that adhere to an absolute theory and those that adopted a restrictive theory. Under the absolute theory, states are absolutely immune from suit in the courts of other states. Under the restrictive theory, states are immune from suits based on their…
Continue ReadingThrowback Thursday: Professor William Casto on the Origins of the Alien Tort Statute
In the spring of 1986, Professor William Casto published an article in the Connecticut Law Review entitled The Federal Courts’ Protective Jurisdiction Over Torts Committed in Violation of the Law of Nations. Casto’s article was the first to explore the origins of the Alien Tort Statute (ATS) in detail, and despite the many law reviewpages…
Continue ReadingOfficials Who Kidnapped Hotel Rwanda Hero Are Not Immune from Suit
In 1994, Paul Rusesabagina was the manager of a hotel in Kigali, Rwanda. During the genocide, he sheltered 1,268 Hutu and Tutsi refugees, all of whom survived. His courage inspired the film “Hotel Rwanda,” and in 2005 President Bush awarded him the Presidential Medal of Freedom. Rusesabagina became a human rights advocate and vocal critic…
Continue ReadingHappy Birthday to TLB!
On March 28, 2022, TLB published its first post. Since then, we have published 245 more. Over the past year, the site has received more than 32,000 visitors from 82 different countries. Roughly half of those readers are based in the United States. Our most frequent non-U.S. visitors are based (in rough order) in (1)…
Continue ReadingCert Petition Highlights Circuit Split on Sovereign Immunity for Military Purchases
The Foreign Sovereign Immunities Act (FSIA) immunizes foreign states from suit in federal and state court. But it makes an exception for actions based on a foreign state’s commercial activities. The Supreme Court’s leading decision interpreting this exception is Republic of Argentina v. Weltover (1992), where the Court unanimously held “that when a foreign government…
Continue Reading